Just like our body, any efficient pumping system requires a strong heart and fully-functioning veins to keep the process running smoothly. In the grand scheme of a pumping system, a foot valve plays a vital role similar to a vein, controlling the flow in the system and preventing back flow. This article aims to shed light on the complexity and operation of a foot valve.
Foot Valve – Essential Component of Efficient Pumping
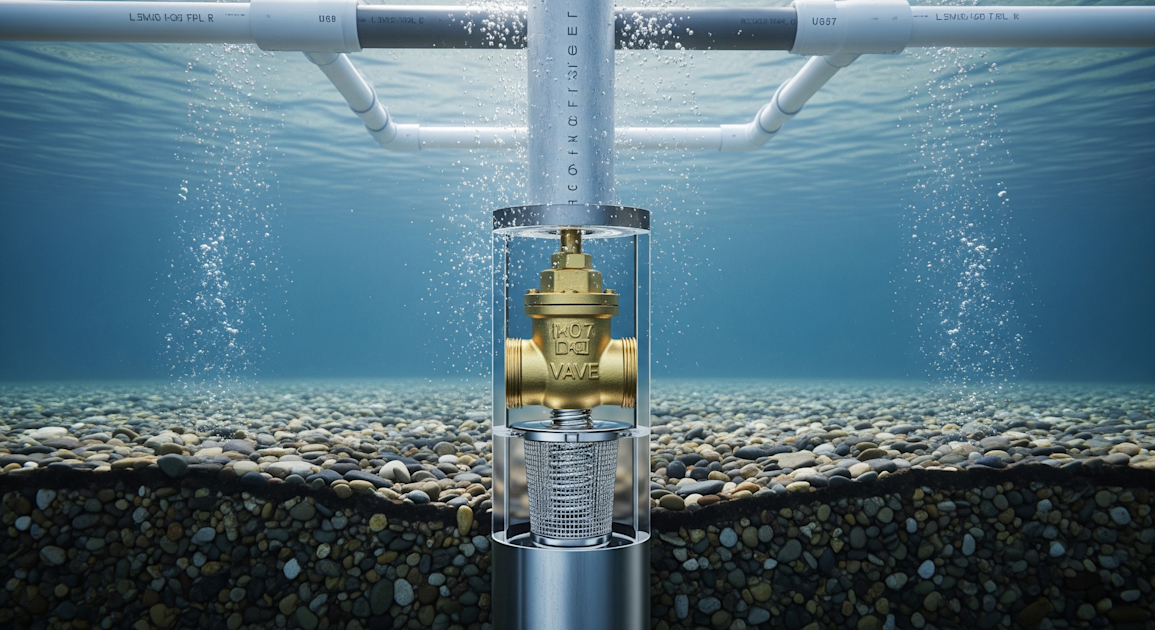
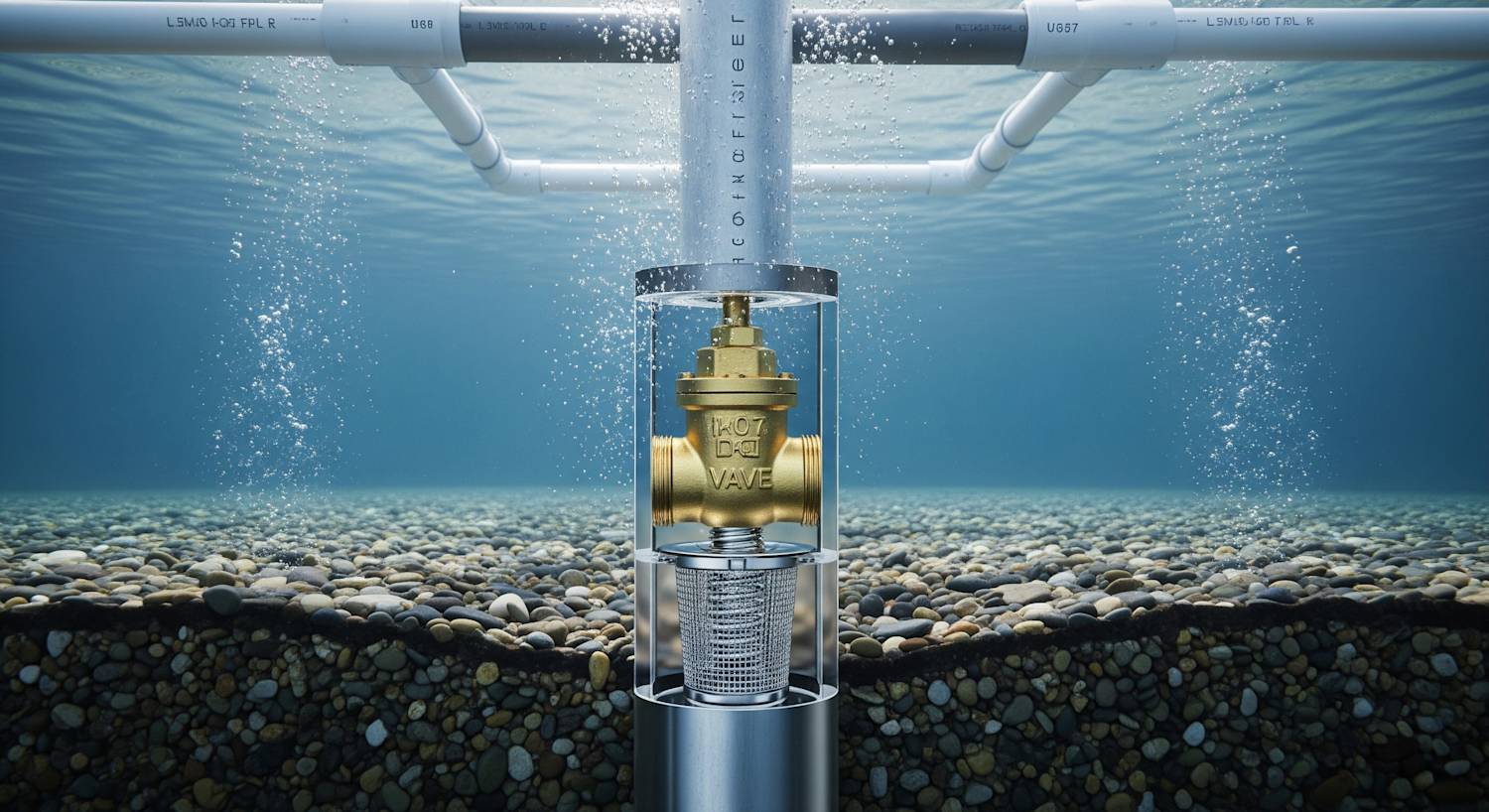
A foot valve is typically a type of one-way check valve located at the bottom of a pump suction line. The primary function of this valve is to permit the fluid (typically water) to flow in one direction, but to prevent it from flowing back in the opposite direction. Thus, the system is continuously primed and ready for effective operation, ensuring the pump's efficiency and longevity.
Why is it Called a Foot Valve?
The name "foot valve" comes from its position in the pumping system. These valves are usually placed at the lower end of the suction pipe, also known as the "foot" – this is where the valve gets its name.
Structure and Operation of a Foot Valve
A foot valve generally consists of the valve body, the disc and the bonnet. The disc is the key element that moves to open and close the valve. Depending on the pressure conditions, the disc opens to let the water flow in, and closes to prevent it from flowing back. The bonnet is attached to the body of the valve, covering the internal mechanisms.
Foot valves are normally constructed with brass, plastic or stainless steel, depending on their application and the type of fluid being pumped.
Key Features of Foot Valves
- Built-in strainer: To prevent debris from entering and damaging the pumping system, foot valves often come with built-in strainers.
- Resilient Sealed Design: This ensures that when the valve closes, it creates a tight seal that maintains the pressure in the system, preventing back flow.
Different Types of Foot Valves
There are various types of foot valves categorized based on the materials used in their construction, their pressure rating, and the function they serve.
- Brass Foot Valves: Offer durability and robustness, best for applications that involve high temperatures.
- Stainless Steel Foot Valves: Known for their corrosion-resistant properties, these are ideal for chemical or saltwater applications.
- PVC Foot Valves: These are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, ideal for lower pressure applications.
Each type serves a unique purpose, and the most suitable variant must be chosen for each application for optimal results.
Foot Valve in Different Industries
Foot valves have a wide range of applications, from simple home-based water systems to heavy industrial applications.
- Agriculture: They are used in irrigation, pond management, and livestock water supply systems.
- Industrial Use: In industries, foot valves are used when dealing with heat transfer equipment, coolers, condensers, and hydraulic elevators.
- Municipal Services: In public water services, foot valves are used in wells, levees, fountains, and water systems.
Along with above, they also find application in marine, construction, and chemical industries.
Maintaining a Foot Valve
Even though foot valves are robust and designed for long-term use, regular maintenance ensures their smooth operation. Routine checkups for internal damages, seal integrity, and valve cleaning add to its operational life. Replace the valve if any abnormalities or severe damages are found.
Frequently Asked Questions about Foot Valve
Why Are Foot Valves Essential in Pump Systems?
Foot valves are essential in many pump systems as they maintain the pump's prime when it's not running. It stops the fluid from draining out of the inlet lines and pump when the pump stops. This helps to ensure that your pump doesn't need repriming each time it runs, which could otherwise result in an inefficient and frustrating operation.
What Are the Common Types of Foot Valves?
There are many types of foot valves available, and they differ based on their size, the materials they are made from, and the pressure they can handle. Common foot valve types include flanged foot valves, socket or threaded foot valves, and swing or spring-assisted check foot valves. The specific type to use largely depends on your pumping requirements, so it's best to consult with a pump or valve professional before making a selection.
Where Can I Install a Foot Valve?
A foot valve is designed to be installed at the bottom of a pump suction line inside the water source like a well, a tank, or a reservoir. This location enables it to maintain the pump prime by keeping a certain level of liquid in the suction line after the pump is turned off.
Can Foot Valves Be Used in High-Temperature Applications?
Some foot valves are designed for high-temperature applications. These are usually made from materials that can withstand high temperatures. However, they may not be applicable for all high-temperature setups. The temperature suitability of a foot valve usually depends on its make, model, and materials used. Always check the specifications or consult with the manufacturer for proper guidance.
How to Correctly Size a Foot Valve?
When correctly sizing a foot valve, it's essential to consider the size of your pump's suction line. Generally, your foot valve's size should match the pump's suction line size. This aligns the valve's capacity with that of the pump and helps reduce the chance of cavitation. Some additional factors to consider include velocity considerations, required flow rates, and system pressure.
How Often Should Foot Valves Be Replaced?
The need for foot valve replacement varies based on several factors, like the level of the water source, the quality of water it processes, and how well the valve is maintained. If a pump frequently loses its prime, struggles to prime, or the performance drops, these could be signs that the foot valve needs replacement.
Pros of Foot Valves
Easy to Install
A significant advantage of foot valves is their relative ease of installation. Even users without extensive technical knowledge can install them successfully. Most of the time, the process only requires some basic tools, along with the right sized pipe, and a thorough reading of the installation instructions. The install process is fairly straightforward and does not typically require professional installation.
Durability
Foot valves are made to last. They are often constructed from robust materials like brass, PVC, or stainless steel that are capable of withstanding various conditions and pressures. This durability allows them to function effectively for many years without significant wear and tear, making them a cost-effective long-term solution for many pumping system setups.
High Resistance to Corrosion
These materials also increase the foot valve's resistance to corrosion. This is a crucial aspect, given that many foot valves are submerged in water for extended periods. Corrosion resistance thus adds to the overall lifespan of the device.
Improved Efficiency
Foot valves play a vital role in maintaining the pump's efficiency by ensuring a constant water supply within the system. They prevent water from flowing back into the source, thus eliminating the need for the pump to draw water afresh every time it's turned on. As a result, they reduce the amount of energy needed to operate the system.
Prevents Debris Entry
Foot valves are typically fitted with filters or screens that prevent debris from entering the pumping system. This feature reduces the risk of damage to the pump and ensures that only clean water reaches the pump and the distribution system.
Cons of Foot Valves
Potential for Failure
Despite their durability, foot valves are not immune to failure. If a foot valve fails, it can prevent the pump from working correctly or at all. The risk of failure increases with heavy utilization, wear and tear, or damage due to debris.
Requires Regular Maintenance
To ensure that a foot valve operates optimally, regular maintenance is essential. Over time, the filter or screen can become clogged by debris, requiring cleaning or replacement. Such maintenance tasks can be time-consuming and may require some level of expertise.
Difficult to Access
One of the considerable disadvantages of foot valves is that they can be challenging to access, given that they are usually placed at the lowest point in the water system, often submerged. As a result, performing routine maintenance or resolving a malfunction can be a daunting task.
Increased System Complexity
While foot valves increase a pumping system’s efficiency, they also add a layer of complexity. Any additional component in a system increases the number of potential failure points, which can increase the system's overall maintenance requirements.
Possibility of Water Hammer
Foot valves can cause a phenomenon known as water hammer. This happens when a valve closes suddenly at the end of a pipeline system, causing a surge of pressure in the direction opposite to the water flow. Over time, this can cause leaks or even destroy other components of the system.
Flow Restrictions
Depending on the design of the foot valve, it can sometimes restrict the flow of water, leading to decreased system performance. It is crucial to choose a foot valve that allows for adequate water passage and is suitable for the pump's specifications to minimize this issue.
Myths and Misunderstandings about Foot Valves
There's considerable misunderstanding about foot valves, their purpose, functionality, installation, and overall worth in various applications. Here, we dispel some prevalent myths and misconceptions that revolve around foot valves.
Myth 1: "Foot Valves Are Only Used in Vertical Pumps."
One common misunderstanding is that foot valves are solely used in vertical pumps. While it’s true that they are generally used in such configurations to keep the pump primed, they are not confined to vertical pump applications alone.
Foot valves can be efficiently applied to various situations where it’s essential to maintain a particular liquid level in the pump. They can also be used in sump pumps, jet pumps, and other pumping systems used for a wide range of applications, from water supply to septic tank systems.
Myth 2: "Foot Valves Are Unnecessary."
Foot valves play a crucial role in many pumping systems. They serve two vital purposes:
Prevent reverse flow: They hold the water being drawn up by the pump to avoid it from flowing back down the system when the pump is off, so the pump remains primed.
Filter debris: They act as a strainer or filter to prevent debris from entering the pumping system, which protects the pump and other related parts from damage.
Without these foot valve features, a pump could lose its prime, causing it to work harder, which significantly increases wear and tear on the pump, and therefore, decreases its lifespan.
Myth 3: "All Foot Valves Operate Similarly."
Foot valves come in different designs and types, and they don’t all operate in the same manner. For instance, some are spring-operated, while others depend on pressure to push the valve open.
These differences in their operation and design impact their suitability for various applications, flow rates, and pressure levels. Understanding the operation of different foot valve designs can aid in selecting the appropriate foot valve for a specific pumping system.
Myth 4: "Foot Valves Are Difficult to Install."
While precise installation is necessary to ensure a foot valve's proper functioning, the process of installing a foot valve is not complicated. Foot valves are typically installed at the bottom of suction lines or at the water source in a pumping system. Care needs to be taken to ensure the foot valve is securely fastened and that the suction line is airtight to prevent the loss of prime.
However, if you’re inexperienced with the installation process, consulting with a professional is recommended for the optimal setup and ensuring the longevity of the pumping system.
Myth 5: "Foot Valves Don't Require Maintenance."
Foot valves are not maintenance-free. Over time, the valve can wear out, get blocked, or fail, thus compromising its effectiveness and risking damaging the pump. Regular inspection is necessary to ensure they remain in good working order, and any signs of leakage or reduced performance should be addressed promptly.
Myth 6: "All Foot Valves Are Made of the Same Material."
Foot valves can be made from a variety of materials, including PVC, bronze, stainless steel, and cast iron. The choice of material affects the valve's durability, corrosion resistance, and its compatibility with different types of fluid. Therefore, it's crucial to select the right material based on the foot valve's intended environment and application.
Selecting the right foot valve can be a daunting task with all the conflicting information available. Understanding these myths and misconceptions can make the task easier and ensure you receive the durability and functionality expected from your foot valve. Remember, every application is unique, and what works for one may not be suitable for another. Hence, consider seeking advice from a knowledgeable professional before making the final foot valve selection.
Summary
A foot valve is an essential piece of equipment with widespread use in a variety of settings. It might seem insignificant but it plays a vital role in maintaining the flow of water in a pump system. Basically, it's like a one-way gatekeeper, keeping water in the pump system from flowing back and ensuring it only goes in one direction. This function optimizes the efficiency and effectiveness of the water system operation.
Moreover, the design of a foot valve is specifically meant to be submerged, often sitting at the bottom of a well or reservoir. Equipped with a check valve, its unique design prevents backflow, which could lead to severe pump damage. Nonetheless, it's crucial to keep an eye on the valve's condition. Even though it's built to last, it can experience wear and tear over time.
Undoubtedly, the foot valve's function and design exhibit its essential role in well and pump systems. Without it, negative consequences like backflow, pump damage, and inefficiency could occur. Therefore, the need to maintain and, if necessary, replace a foot valve over time cannot be underestimated. It's a small component that holds a significant role in any water pump system setup.
About KYPD Plumbing
KYPD Plumbing is a trusted and go-to plumbing company based right in the heart of Lexington, KY. We've been proudly serving the local community and beyond for several years, providing high-quality, reliable and prompt services. Our team of licensed and experienced plumbers always goes above and beyond to ensure that every issue, whether big or small, is handled with utmost precision and efficiency. Whether it's a dripping faucet, a clogged drain, or a major pipe burst, you can rely on KYPD Plumbing to deliver exceptional services that not only meet, but exceed your expectations.
Tags: valve, plumbing, pump,